A modified efficient purse-string stapling technique (mEST) that uses a new metal rod for intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy in laparoscopic total gastrectomy
Since laparoscopic distal gastrectomy was first reported by Kitano et al., laparoscopic approaches have been widely used to treat early gastric malignancies (1). Such approaches have been applied to total gastrectomy for the treatment of gastric cancers located in the upper third of the stomach. In laparoscopically assisted total gastrectomy, reconstruction procedures have commonly been performed using a circular stapling device under direct vision via a small upper-abdominal laparotomy (2), which is sometimes difficult, particularly in cases involving obese patients with thick abdominal walls. Therefore, surgeons have been eager to perform intracorporeal anastomosis (3). However, esophagojejunostomy in Roux-en-Y reconstruction after laparoscopic total gastrectomy is technically demanding because this procedure should be performed in a narrow surgical field in the upper abdomen, even when completely laparoscopic approaches are used. Therefore, we developed a simple technique for intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy using a circular stapling device; we named this approach the efficient purse-string stapling technique (EST) (4-7). We first reported this original technique for laparoscopic Billroth I gastrectomy in 2005 (4). Subsequently, this technique was applied to Roux-en-Y reconstruction in laparoscopic distal or total gastrectomy with a hemi-double stapling technique in 2007 (5,6). In addition, we applied the EST to single-incision laparoscopic Billroth I gastrectomy (7). The application of EST has been extended to laparoscopic colorectal surgery (8,9). More recently, in 2013, we developed a modified EST (mEST) involving the use of a newly created metal device (Endo Mini Rod, Takasago Medical Industry, Tokyo, Japan). In this paper, we describe the technical details of this procedure, including relevant skills and pitfalls.
Surgical TechniquesOther Section
Patient positioning and OR setting
The patient was placed in the supine position with the legs opened. The surgeon, the first assistant, and the scope assistant were positioned on the right side of the patient, the left side of the patient, and between the patient’s legs, respectively. The nurse stood near the patient’s left leg. A laparoscopic unit with a monitor was located above the patient’s shoulders.
Port setting
An umbilical laparotomy through a 2.5- to 3.0-cm vertical skin incision in the umbilicus was made using the open method. A mini-laparotomy was made using a wound sealing device (Lap protector, Hakko, Nagano, Japan), which was covered by an access port (EZ access; Hakko, Nagano, Japan) with a trocar for insertion of the laparoscope. A 12-mm trocar was inserted into the anterior axillary line of the right subcostal space, a 5-mm trocar was inserted into the right lateral abdomen for the main surgeon, and 5-mm trocars were inserted into the left subcostal space and left lateral abdomen for the first assistant.
Technique
The patient was placed in the reverse Trendelenburg position with the legs apart. During the procedure, pneumoperitoneum was established with carbon dioxide insufflations at a pressure level of approximately 8 to 12 mmHg, based on the patient’s body type. A 10-mm flexible high-definition scope (Endoeye flexible HD camera system; Olympus Medical Systems Corp.) was used to visualize surgical fields. The greater curvature was dissected, and the left gastroepiploic vessels were clipped and divided for the dissection of station 4sb lymph nodes. The gastrosplenic ligament was divided using laparoscopic coagulating shears for the dissection of station 4sa lymph nodes. The right gastroepiploic vein and artery were transected for the dissection of station 6 lymph nodes.
Suprapancreatic lymph node dissection using the cranial approach
We commonly use the cranial-to-caudal approach (the cranial approach) in multiport laparoscopic gastrectomy as well as single port laparoscopic gastrectomy (10), in which the stomach and the distal pancreas are first mobilized from Gerota’s fascia prior to the lymphadenectomy procedure.
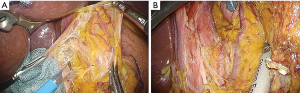
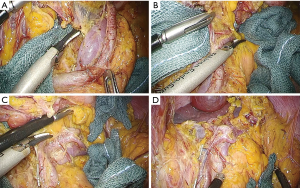
During dissection at stations 8a and 12a, the common hepatic artery, the bifurcations of the proper hepatic and gastroduodenal arteries, and the portal vein were exposed along the plane of the periarterial plexus for lymph node dissection. After the dissection of lymph nodes at stations 5, 8a, 9, and 12a, the peritoneum was incised at the level of the right crus of the diaphragm, and the left gastric artery was then clipped and divided (Figure 1A). The mesogastrium was retracted anteriorly to dissect the plane between Gerota’s fascia and Toldt’s fusion fascia laterally and caudally (Figure 1B). Subsequently, the esophagus was transected using a linear stapling device (ECELON FLEX Powered ENDOPATH Stapler, Ethicon Endosurgery, Cincinnati, OH, USA). This full mobilization of the splenic artery (mesenterization) allowed for the easy dissection of 11p/11d lymph nodes under excellent surgical views. Lymph nodes at station 11p were dissected in the dorsal plane, where the splenic vein or pancreas could be identified (Figure 2A). Posterior gastric vessels were identified and divided after clipping (Figure 2B). Dissection of 11d lymph nodes was performed along the distal pancreatic artery toward the splenic hilum (Figure 2C,D). The resected specimen was then extracted through a small incision.
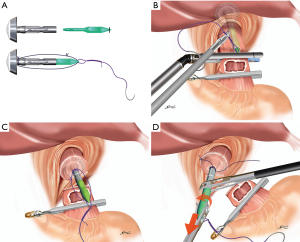
Anvil placement into the proximal esophagus using the EST
The placement of the anvil of a circular stapling device (ECS 25, Ethicon Endosurgery, Cincinnati, OH, USA) into the esophagus is one of the most difficult steps in this surgery. We have commonly used our original technique, the EST, for this anvil placement (5). In this technique, the anvil with a green plastic rod sutured to a needle and thread (Figure 3A) is completely inserted into the esophagus. The needle and thread are used to penetrate the anterior wall of the esophagus (Figure 3B). Finally, the esophagus is transected using a linear stapling device with a 60-mm blue cartridge (ECELON FLEX Powered ENDOPATH Stapler, Ethicon Endosurgery, Cincinnati, OH, USA) just distal to the needle penetration site (Figure 3C), and the anvil placement procedure is completed after the removal of the rod from the anvil (Figure 3D).
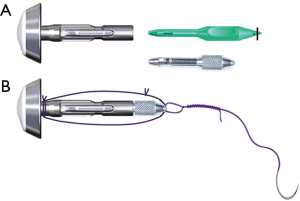
Insertion of the anvil into the esophagus
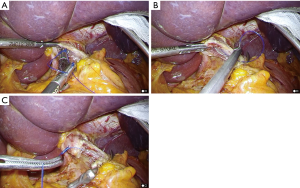
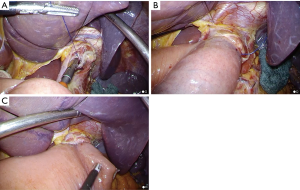
In preparation for this procedure, a stainless steel rod (Endo Mini Rod, Takasago Medical Industry, Tokyo, Japan) was attached to the shaft of the anvil, and a thread with a needle was then sutured to the tip of the rod. We used a stainless steel rod instead of a green plastic rod. Relative to the plastic rod, the steel rod is reusable and shorter; thus, it was easier to perform anvil placement into the esophagus with the steel rod (Figure 4). After the distal esophagus was clamped using a detachable intestinal holder forceps (Figure 5A), a hemicircumferential esophagotomy was performed on the anterior esophagus (Figure 5B). The anvil head was placed over the window (Figure 5C), and the anterior wall of the esophagus was fixed by covering it with the anvil head (Figure 5D). The anvil with the rod was pushed cranially along the esophageal cavity and completely inserted into the esophagus (Figure 6A).
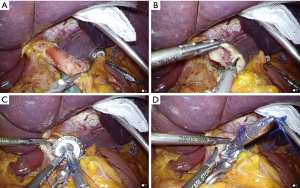
Placement of the anvil in the esophagus
The needle penetrated the anterior wall of the esophagus 1 cm proximal to the esophagotomy (Figure 6B), and the thread was pulled out until the ligation knot was exteriorized from the esophageal cavity (Figure 6C). The proximal esophagus was transected using a linear stapling device (ECELON FLEX Powered ENDOPATH Stapler, Ethicon Endosurgery, Cincinnati, OH, USA) just distal to the site penetrated by the thread, and anvil placement in the esophagus was simultaneously completed (Figure 7).
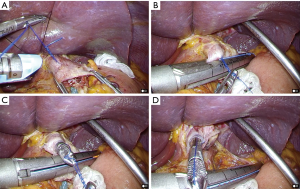
Esophagojejunostomy
After the body of the instrument was inserted into the umbilical wound via the EZ access port, CO2 insufflation was re-established. After the rod was removed from the anvil (Figure 8), the instrument was intracorporeally connected to the anvil and then fired to complete the gastrojejunostomy (Figure 9). The stump of the jejunum was closed using a linear stapling device (Figure 9).
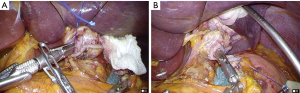
CommentsOther Section
In this paper, step-by-step procedures for laparoscopic total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction using the mEST were described. This technique is simple and may facilitate intracorporeal reconstruction procedures in laparoscopic total gastrectomy. In addition, mEST can be applied to all reconstructive procedures for laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery.
AcknowledgementsOther Section
None.
FootnoteOther Section
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
ReferencesOther Section
- Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, et al. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1994;4:146-8. [PubMed]
- Omori T, Nakajima K, Endo S, et al. Laparoscopically assisted total gastrectomy with jejunal pouch interposition. Surg Endosc 2006;20:1497-500. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kunisaki C, Makino H, Oshima T, et al. Application of the transorally inserted anvil (OrVil) after laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy. Surg Endosc 2011;25:1300-5. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Omori T, Nakajima K, Nishida T, et al. A simple technique for circular-stapled Billroth I reconstruction in laparoscopic gastrectomy. Surg Endosc 2005;19:734-6. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Omori T, Oyama T, Mizutani S, et al. A simple and safe technique for esophagojejunostomy using hemi-double stapling technique in laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy. Am J Surg 2009;197:e13-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Omori T, Oyama T, Akamatsu H, et al. A Simple and Safe Method for Gastrojejunostomy in Laparoscopic Distal Gastrectomy Using the Hemidouble-Stapling Technique: Efficient Purse-String Stapling Technique. Dig Surg 2009;26:441-5. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Omori T, Tanaka K, Tori M, et al. Intracorporeal circular-stapled Billroth I anastomosis in single-incision laparoscopic distal gastrectomy. Surg Endosc 2012;26:1490-4. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu H, Omori T, Oyama T, et al. Totally laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy: a simple and safe technique for intracorporeal anastomosis. Surg Endosc 2009;23:2605-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu H, Omori T, Oyama T, et al. Totally laparoscopic low anterior resection for lower rectal cancer: combination of a new technique for intracorporeal anastomosis with prolapsing technique. Dig Surg 2009;26:446-50. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Omori T, Nishida T. Distal Gastrectomy. In: Mori T, Dapri G, editors. Reduced Port Laparoscopic Surgery. Tokyo: Springer; 2014:183-95.
Cite this article as: Omori T, Moon JH, Yamamoto K, Yanagimoto Y, Sugimura K, Miyata H, Yano M, Sakon M. A modified efficient purse-string stapling technique (mEST) that uses a new metal rod for intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy in laparoscopic total gastrectomy. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2:61.


